
The Sauber C9 (later named the Sauber Mercedes C9 or Mercedes-Benz C9) is a Group C prototype racing car introduced in 1987 as a continuation of the partnership between Sauber as a constructor and Mercedes-Benz as an engine builder for the World Sportscar Championship. The C9 replaced the Sauber C8.

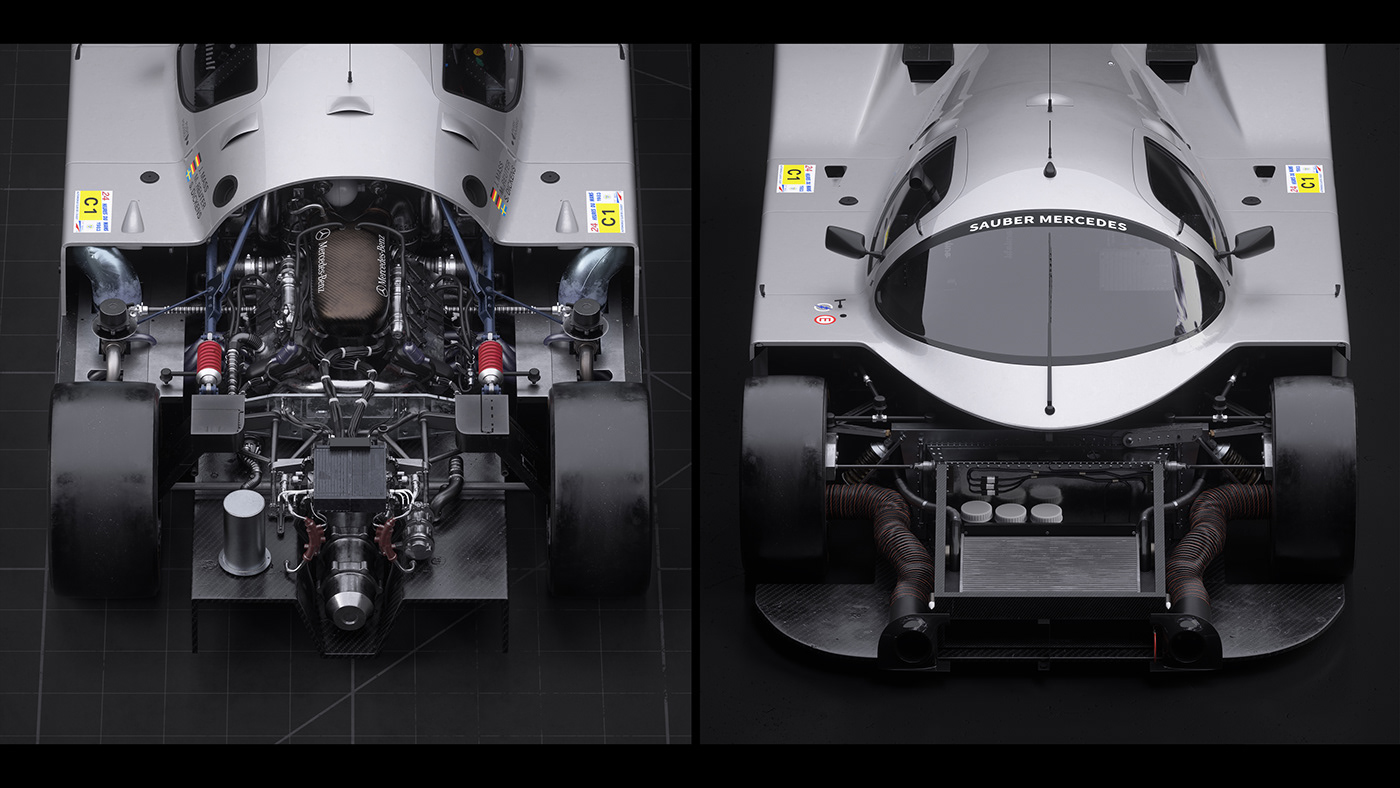



The C9 was a development of Sauber's previous C8 design, retaining a monocoque that largely consisted of aluminium, although considerably stiffer and with numerous other improvements. The rear suspension changed from vertically positioned spring/damper units arranged over the top of the gearbox to a horizontal layout aligned with the longitudinal axis of the car. Aerodynamic changes included the repositioning of the combination of oil/water radiator to the nose of the car, which allowed the use of a modified splitter plate. Commensurate with the repositioning of the radiators, the large NACA ducts were removed from the top of the door sills. The rear deck had been considerably re-profiled and the rear wing was now mounted solely on a central support. Aerodynamically, the car had two configurations: one for sprint circuits and a low drag version for the 5.8 kilometre Mulsanne Straight at Le Mans. In its sprint configuration, it produced 2,222.1 kg (4,899 lb) of downforce at 320 km/h (200 mph) while generating 555.7 kg (1,225 lb) of drag. The sprint circuit configuration had a L/D ratio of 4:1 while the low drag version was around 3:1.[1] The early engines were again prepared by Swiss engine specialist, Heini Mader, though this is now known to have been a cover for Mercedes back door involvement with the project later on. It had been progressively lightened with the use of a new crankshaft, higher efficiency KKK turbochargers and a liner-less block. It was a semi-stressed part of the chassis and ran a dry sump. There were no special qualifying engines and on 2.2 bar of boost it was said to be rated at "almost 800 hp (811 PS; 597 kW)". Maximum race boost was 1.9 bar. Maximum RPM was 7,000 but drivers generally kept to 6,500 during races. The torque curve was almost uniform between 3,000 and 6,000 rpm, giving the engine plenty of flexibility.[2] The engine retained a cross plane crankshaft and the firing order was 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2. Later M119HL engines were sourced from the Mercedes engine facility at Untertürkheim, supervised by Hermann Hiereth.[3] The addition of 16 valve heads in 1989 took power up by about 20 hp (20 PS; 15 kW) to around 720 hp (730 PS; 537 kW) at 1.6 bar and 7,000 RPM. The increase in fuel efficiency meant absolute power could also be taken from just under 800 hp with 2.2 bar of boost to about 820 hp (831 PS; 611 kW).[4]


Reference






Thanks!


